Taxonomy: Kingdom - Plantae (plants). Subkingdom - Tracheobionta (vascular plants). Superdivision - Spermatophyta (seed plants). Division - Magnoliophyta ( Flowering plants). Class - Magnoliopsida. Order - Sapindales. Family - Sapindaceae (Maple family). Genus -Acer L. Species - Acer grandidentatum Nutt.
Ecology: Bigtooth maple is a deciduous, small tree or shrub of variable size. Its life form is dependent upon the moisture regime. In canyon bottoms and along streams it grows as a tree with single or multiple trunks reaching 15 m tall and 30 cm in diameter, while on dry canyon slopes it grows as a shrub with 2 or more stems reaching 8 m tall. Bigtooth maple leaves are palmately lobed, 2.5-10 cm wide, and pubescent beneath.
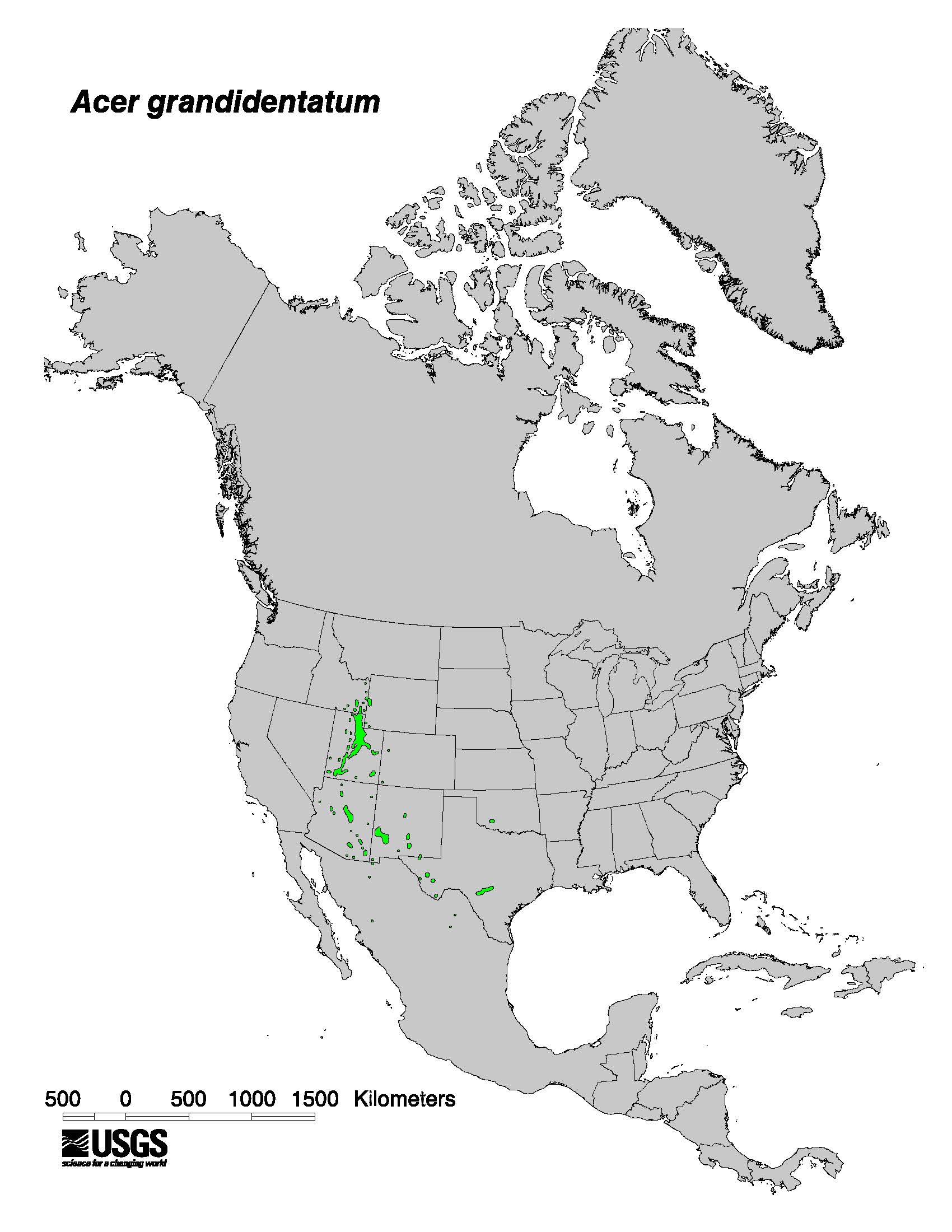
Bigtooth maple has a broad ecological amplitude. It occurs on a wide range of sites with different aspects, soil types, and soil moisture conditions. Throughout its range it is most often located on cool, moist sites in canyons, ravines, along mountain streams, and on lower slopes...When bigtooth maple grows together with Gambel oak, it occupies ravines while Gambel oak occupies the slopes.
Bigtooth maple is an early- to late-successional species. It is abundant in late successional riparian communities in Zion National Park, Utah. Seedlings are shade tolerant and grow under the canopy of mature big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) and Gambel oak...Bigtooth maple commonly invades Gambel oak stands in Utah and northern Arizona...Because bigtooth maple leafs and flowers earlier and grows faster in stem and crown diameter than Gambel oak, it becomes more important in the canopy over time. On some sites, it may eventually replace Gambel oak. Bigtooth maple is the dominant climax species in many maple-oak woodlands from north-central Utah to south-central Idaho.