Taxonomy: Kingdom - Plantae (plants). Subkingdom - Tracheobionta (vascular plants). Superdivision - Spermatophyta (seed plants). Division - Coniferophyta (conifers). Class - Pinopsida Order - Pinales Family - Cupressaceae (cypress family). Genus - Sequoia Endl. (redwood ). Species - Sequoia sempervirens (Lamb. ex D. Don) Endl. (redwood).
Ecology: Redwood is a native, evergreen, long-lived (greater than 2,200 years), monoecious tree. Redwoods are among the world's tallest trees; trees over 61 m are common, and many are ove 91 m. The largest tree thus far was measured at 110.3 m in height and 6.1 m in d.b.h. The root system is composed of deep, widespreading lateral roots with no taproot. The bark is up to 30 cm thick and quite fibrous. Redwood self-prunes well in dense stands; the base of the bole is strongly buttressed.
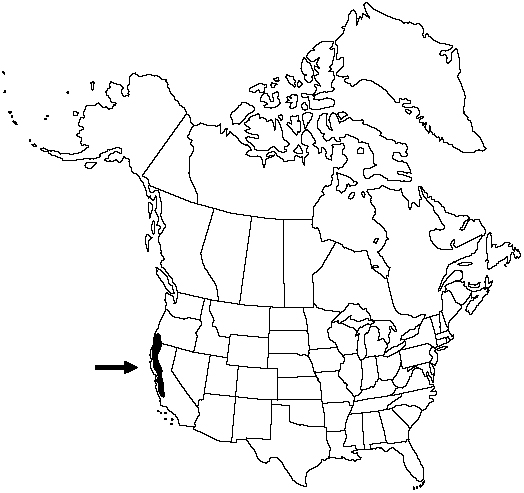
Redwood is endemic to the coastal area of northern California and southwestern Oregon. Redwood is one of California's most valuable timber species. The wood is soft, weak, easily split, and very resistant to decay. The redwoods occupy a narrow strip of land approximately 724 km in length and 8-56 km in width.Redwood occurs in a maritime Mediterranean climate, where the winters are cool and rainy, and the summers are dry. The dry summers are mitigated by a heavy fog belt. The fog reduces the drought stress of this hydrophilic plant by reducing evapotranspiration and adding soil moisture.
Redwood is classified as a shade-tolerant to very shade-tolerant species due to its high photosynthetic capacity at low light levels. There is some debate over the classification of redwood as a climax species. Some consider redwood a climax species, while others consider it a fire-dependent seral species. After disturbance redwood dominates in early seres due to its ability to sprout.
Redwood is long lived, grows taller than any other tree species in the world, and is exceeded in bulk only by the giant sequoia. Redwoods are sexually mature at 10 years or less but continue to increase in volume for centuries. Under some conditions, redwood can endure suppression almost indefinitely. A 25-cm suppressed tree might be more than 100 years old. Small trees may be suppressed for more than 400 years but still maintain a remarkable capacity to accelerate growth rates when released if they have not been crowded too closely and are not injured seriously during logging or slash burning. Large trees also can accelerate growth when released from competition.